Time : July 11, 2023
Abstract: This article summarizes the research and development status of ceramic rolling bearings both domestically and internationally, focusing on the preparation and processing technologies of ceramic balls and ceramic rings, and pointing out the future research directions of ceramic bearings.
Keywords: ceramic bearings, rolling bearings, ceramic materials, machining centers
1 The necessity and urgency of developing new ceramic bearings
With the development of the mechanical industry towards high-precision, high-efficiency, and highly automated directions, the working speeds of various machines continue to increase. For example, the spindle speed of CNC machining centers has increased from 5000 rpm in the 1980s to 25,000~30,000 rpm now. The dn value (product of bearing diameter and speed) of high speeds has reached 3 million, and the experimental value has reached 3.5~4 million. Machinery that operates in certain high-tech fields and special environments, such as the aerospace industry, nuclear energy industry, chemical industry, petroleum industry, food industry, etc., needs to work in special environments such as high temperature, high speed, corrosion resistance, vacuum, non-magnetic, oil-free lubrication, and light weight. Nowadays, steel bearings cannot meet these requirements. The main problem with high-speed bearings is the decrease in bearing life, increase in temperature rise, decrease in stiffness and accuracy caused by high-speed, and the large centrifugal force caused by rolling balls. This centrifugal force causes the pressure between the ball and the outer ring raceway to even exceed the effect of external loads, thereby reducing the bearing life. At the same time, too high rotating speed will exert a large gyroscopic torque on the ball, which will make the ball and the ring slip, increase the Friction torque, increase the heating and generate additional pressure on the cage, resulting in large temperature rise and cage damage. Therefore, the needs of high-speed machinery and special working environments such as high temperature and corrosion resistance cannot be met solely by improving the structure and lubrication conditions of current steel bearings. It is necessary to make fundamental breakthroughs and innovations in ceramic materials, research and development of new materials for bearings, in order to meet the requirements of high-tech and industrial production development.
As a modern high-tech new material, engineering ceramics have developed rapidly and their technology is becoming increasingly mature. It has wear resistance, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, low magnetic density (only about 40% of bearing steel), low thermal expansion coefficient (25% of bearing steel), and high elasticity coefficient (1.5 times that of bearing steel), ceramic bearings made of ceramic materials are very suitable for working in special environments such as high speed, high temperature, and corrosion resistance. Because of its low density, using ceramic balls as rollers can greatly reduce centrifugal force and gyroscopic torque at high speed, thus greatly reducing the pressure and Friction torque on the outer ring of the bearing, and improving the service life of the bearing. Experimental studies have shown that compared with steel bearings of the same specification and accuracy level, hybrid ceramic bearings can increase their lifespan by 3-6 times and reduce their temperature rise by 35-60%. There are two types of ceramic bearings: hybrid ceramic bearings and all ceramic bearings. The former is made of ceramic material as the ball or column of the rolling element, while the inner and outer rings are still made of bearing steel; Or both the rolling element and inner ring are made of ceramic material, while the outer ring is still made of bearing steel; All ceramic bearings, on the other hand, are made of ceramic for both the rolling element and inner and outer rings. At present, the high-speed ceramic bearings developed and applied internationally are mainly hybrid types, which are made of ceramic materials for balls or columns, and the inner and outer rings are still made of bearing steel. Due to the high brittleness and easy damage of ceramic materials, and the poor reliability of making inner and outer rings, all ceramic bearings have not yet reached the practical stage.
Since the successful development of ceramic bearings in the United States in 1972, Japan and Germany have been catching up and quickly developing. Ceramic bearings have made remarkable achievements from scratch, from experimental research to industrial production, from high confidentiality to public sales. This is a high-tech product that intersects mechanical manufacturing technology and material science. At the 16th Japan International Machine Tool Expo in Tokyo in 1992, a series of physical products of ceramic rolling bearings were publicly displayed and accepted orders from users. Some machine tool manufacturers have also exhibited machining centers and ultra precision machine tools that use ceramic bearings for high-speed cutting of the spindle. The application of ceramic bearings in machine tools is developing fastest in Japan. In recent years, spindle components such as MC56-5XA machining center (15000 rpm) produced by Makino Company, MV -65A/40 machining center (25000 rpm) produced by DMG Mori Seiki Co. Company, UHS10 machining center (100000 rpm) produced by Niigata Iron Company, and HPM – type ultra precision lathe (150 * 150mm) produced by Kyocers Company of Japan have all adopted hybrid ceramic rolling bearings. FAG and SKF companies in Germany have produced a series of ceramic bearing spindle units. The successful development of ceramic rolling bearings in the United States has reached a service temperature of 800 ° C, the DN value of hybrid ceramic bearings in Japan has reached 2.5 million, and the DN value of all ceramic bearings has reached 2.12 million. At present, in addition to the application of ceramic bearings in precision machine tool main bearings, ceramic bearings have also been tried in machinery such as combustion oxygen turbine engines and vacuum pumps internationally. However, mixed ceramic bearings (with Si3N4 ceramic balls or columns) are mainly used, and all ceramic bearings are still in the experimental stage and have not been applied in practice. Since 1990, basic research on ceramic bearings has been carried out in some universities in China, such as Guangdong Institute of Technology; precision machining experiments on ceramic balls have been carried out in Northeast University, Shenyang Institute of Construction and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Tianjin University, etc.; and research and performance experiments on hybrid ceramic bearings (made of Si3N4 and supplied by Shandong Zibo Ceramic Research Institute) have been carried out in Harbin Institute of Technology, Guangdong Institute of Technology and Luoyang Bearing Research Institute are collaborating on the research and development of ceramic bearings. In short, the research on ceramic bearings started relatively late in China, and currently it is still in the experimental research stage in the field of hybrid ceramic bearings. No products have been successfully developed, and no experimental work has been carried out on all ceramic bearings except for basic research. From the situation of hybrid ceramic bearings that have been applied internationally, the effect is very significant. The most prominent is that they have solved the problem of developing new machine tools for high-speed and ultra-high precision machining, and the bearing life has been increased by 3-6 times compared to steel bearings. At present, the price ratio of hybrid ceramic bearings to steel bearings has been reduced from 10:1 to 2.5: 1.
3.1 Preparation Technology of Ceramic Balls
At present, the main ceramic balls in China include Si3N4 ceramic balls, ZrO2 ceramic balls, and Al2O3 ceramic balls. The units that can prepare ceramic ball blanks are mainly concentrated in scientific research institutions, such as Shandong Industrial Ceramic Research and Design Institute and Luoyang Bearing Research Institute. They are still in the stage of small-scale production in the laboratory and have not yet formed industrialized large-scale production. In the process of preparing ceramic ball blanks, in order to improve the shape accuracy, size accuracy and high density of ceramic ball blanks, the Hot isostatic pressing method is generally used, that is, the high-pressure gas is used to transfer pressure to initially compact the blanks to form ceramic ball blanks, and then high-temperature sintering is carried out in high-pressure nitrogen, argon or hydrogen; Alternatively, a cold isostatic pressing machine can first perform cold isostatic pressing on ceramic powder, followed by pressureless sintering.
3.2 Processing Technology of Ceramic Balls
At present, the demand for ceramic balls is very small, so batch processing has not been formed yet. The units conducting research on ceramic balls have the ability to process ceramic balls in a small batch. There are few units that can process ceramic balls in a real batch. For example, Wulian County Steel Ball Factory in Shandong Province has jointly built a ceramic ball finishing workshop with Taiwan Province, which has the ability to supply high-precision (G5, G10, G16, G20, etc.) ceramic balls in batches, However, due to the relatively small demand for ceramic balls in China, the production workshop is basically in a state of shutdown. Due to its minimum processing capacity of 30000 ceramic balls at a time and the company’s unwillingness to stock them, it cannot meet the small purchase volume requirements of most users.
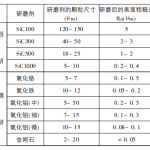
The processing method and equipment for general ceramic balls are similar to the processing of steel ball blanks, but the difference lies in the differences between grinding tools and abrasives. Due to the large shape and size errors of ceramic ball blanks and the abundance of surface defects, the processing of ceramic balls generally involves two stages: grinding and grinding. Grinding is completed on a ball grinder and can be done using SiC or diamond grinding wheels. The precision that Si3N4 ceramic balls can achieve after grinding is: diameter variation, spherical deviation of 70-80 um, and surface roughness of Ra2-3 um. In addition, ceramic balls can be directly ground and processed on a regular grinding machine, but the abrasive used for grinding is different from that used for processing steel balls. Grinding can be divided into rough grinding, semi precision grinding, precision grinding, and ultra precision grinding. The abrasives used for rough and fine grinding, as well as their particle size and achievable surface roughness, are listed in Table 1.
The guide fluid can generally be mixed with petroleum, grease, engine oil, wax, latex water, and alcohol in a certain proportion, with a certain viscosity, and then mixed with grinding agent to form the grinding fluid. The precision that Si3N4 ceramic balls can achieve after grinding is: diameter variation and spherical deviation of 0.04-0.08 m, with a surface roughness of Ra0.004-0.008 um, has reached and exceeded the quality standards for Level 3 balls.
Table 1 Selection of Abrasive for Grinding Si3N4 Ceramic Balls
In China, Northeastern University and Northwestern Polytechnical University have experimented and studied the V-groove grinding method. The disadvantages of this method are low grinding efficiency and slow spherical error correction. On the basis of the traditional V-groove grinding method, Kanazawa University of Japan designed the spin angle control grinding method, which is characterized by controlling the spin angle of the ball, enhancing the spin movement of the ball, and improving the sphericity and submergence efficiency. Subsequently, Japan developed a new method for grinding ceramic balls, the magnetic fluid grinding method, which has a high grinding efficiency, about 50 times that of the ordinary V-groove grinding method. In 1997, Northeastern University 2 conducted experiments on a new grinding method for ceramic balls, namely the conical grinding method, based on domestic and international research. A systematic study was conducted on the grinding mechanism, grinding process, and accuracy of ceramic balls.
4 Preparation and Processing Technology of Ceramic Ferrules
4.1 Preparation Technology of Ceramic Ferrules
At present, Si3N4 ceramic is the main material for ceramic rolling bearing rings, and its preparation technology is much more complex than ceramic balls. A better preparation method is to first use a cold isostatic press and a certain shape of mold to press the ceramic powder into a bearing ring green with a certain strength and hardness, then use a lathe to process the raceways and chamfers on the inner and outer bearing rings, and finally conduct pressureless sintering to obtain the required ceramic bearing ring blank, For further precision processing. Domestic research in this field started relatively late, and there is no ceramic bearing ring that can be really prepared and used by this production process. At present, Shandong University of Technology is developing a new type of ceramic material for bearing by taking advantage of the technical advantages and advanced equipment foundation (such as cold isostatic press and hot pressing sintering furnace) that have developed ceramic tools for many years, to overcome the shortcomings of low strength and poor fatigue resistance of ceramic bearing rings at present. At present, most ceramic bearing rings are prepared using the hot pressing sintering process. The disadvantage of this method is that it cannot pre machine the raceway and chamfer, and relies solely on grinding for processing. This results in high production costs and high processing difficulty.
4.2 Processing Technology of Ceramic Ferrules
The processing technology of ceramic bearing rings is greatly different from that of steel bearing rings. Due to the fact that ceramic bearings are generally limited to use in high-speed precision components and mechanical equipment operating in special environments (such as high temperature, corrosion resistance, light weight, non magnetic, etc.), their production batch cannot be large. Therefore, the grinding of ceramic rings is generally carried out on high stiffness cylindrical or inner cylindrical grinding machines, with processes divided into coarse grinding, fine grinding, grinding, and polishing. The coarse grinding particle size is 120/140 #, and the fine grinding is 270/400 #, Grinding is carried out using fine-grained precision grinding discs on a grinding machine. The polishing operation generally uses a soft polishing tool and diamond micro powder with fine grinding particles (4 um). After polishing, the surface roughness of the ceramic ring can reach Ra0.04-0.1um. Moreover, ceramic ferrules are generally non conductive and cannot be machined by electricity; Non magnetic, cannot use magnetic fixtures. Therefore, during rough grinding, a pressure disc is generally used for mechanical clamping, while during fine grinding, an expanded tire mandrel is used for hydraulic clamping. Generally, diamond grinding wheels are used, and diamond grinding wheels with ceramic binders have the best grinding effect. In order to achieve a lower surface roughness (Ra0 1 m), sometimes diamond honing is used.
5 Outlook
Although the research on ceramic bearings in China started relatively late and is still in the experimental stage, especially for all ceramic bearings, it has attracted high attention from the Chinese government. Many universities and research institutions in China are working hard to research and develop ceramic bearings, so it is imperative to research and develop ceramic bearings. To make this high-tech product practical in China as soon as possible, research must be focused on the following aspects:
More about XZBRG Cylindrical roller bearings:
Cylindrical roller bearings are also available in sealed or split designs. In sealed bearings, the rollers are protected from contaminants, water and dust, while providing lubricant retention and contaminant exclusion. This provides lower friction and longer service life. Split bearings are intended primarily for bearing arrangements which are difficult to access, such as crank shafts, where they simplify maintenance and replacements.
